::
Transforming Patient Care with LLMs: A Research Stack
This stack is a dedicated repository of experiments, research insights, and practical implementations exploring the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) in medical and patient care contexts. From clinical decision support to patient interaction tools, the work documented here investigates how state-of-the-art language models like GPT can enhance healthcare delivery, improve accessibility, and support medical professionals. The goal is to bridge the gap between AI innovation and real-world clinical needs, with a focus on ethical, safe, and impactful applications.

Researchers: LLM-Produced Discharge Summaries Comparable to MD-Produced Ones
A study published in JAMA Internal Medicine points to potential AI support for hospitalists Can discharge summaries produced using large-language models (LLMs) actually match the accuracy and patient safety of discharge summaries produced by human physicians?
- ➔ Across 100 encounters
- ➔ LLM- and physician-generated narratives were comparable in overall quality
- ➔ LLM-generated narratives were more concise
- ➔ There was no significant difference n the potential for harm between LLM- and physician-generated narratives across individual errors
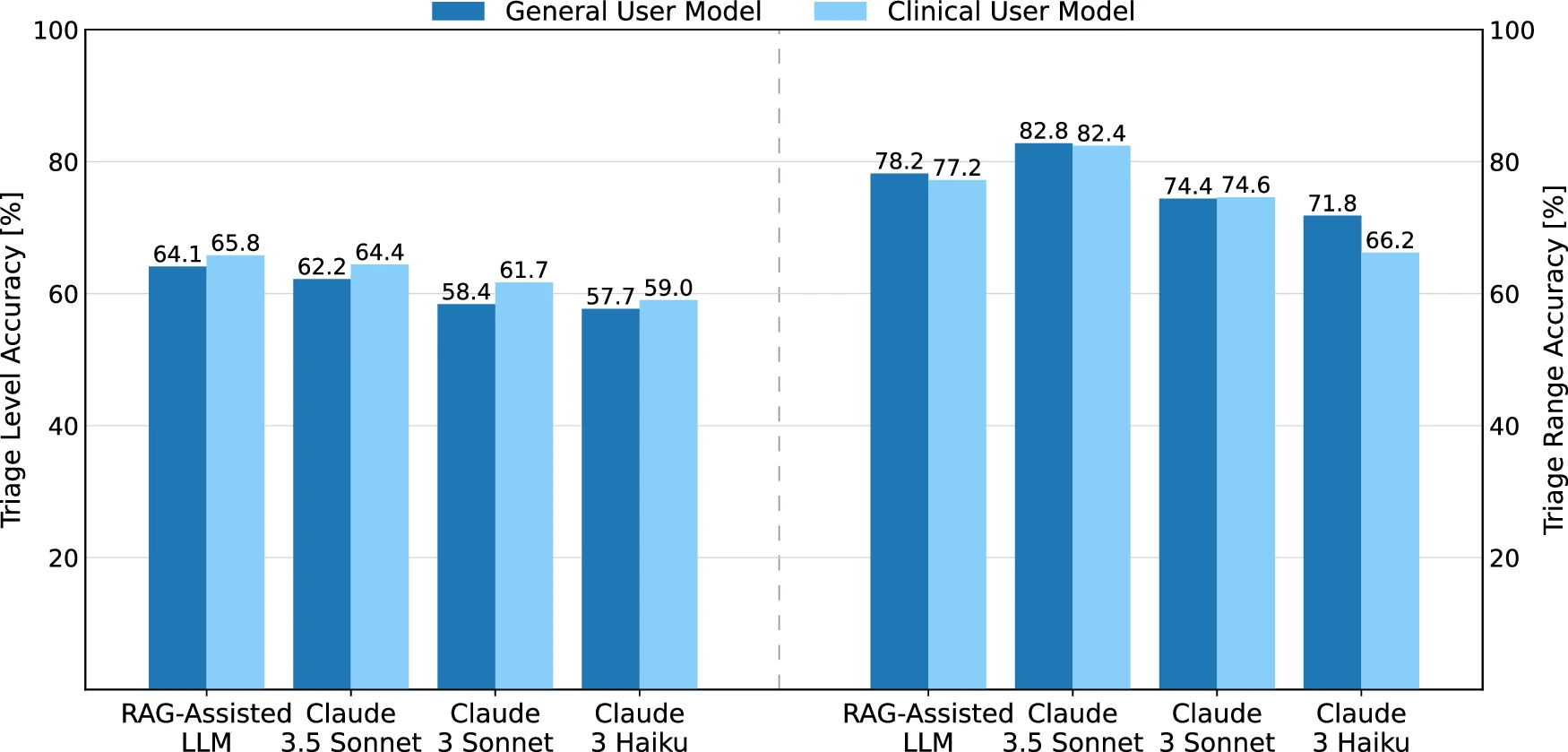
Evaluating large language model workflows in clinical decision support for triage and referral and diagnosis
In this study, we benchmark multiple LLM versions and an LLM-based workflow incorporating retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) on a curated dataset of 2000 medical cases derived from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care database. Our findings show that these LLMs are capable of providing personalized insights into likely diagnoses, suggesting appropriate specialists, and assessing urgent care needs.